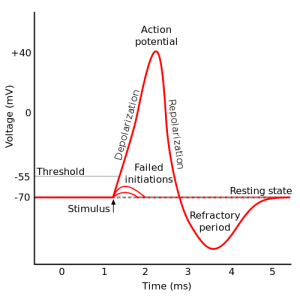
Repolarization is the process by which the neuron regains its negative resting membrane potential. Repolarization starts between +30 and +40 mV. In this range, voltage-gated sodium channels will close and voltage-gated potassium channels will open. This allows positively-charged potassium ions that are in high concentration in the cell to leave. The membrane potential will drop past the resting potential before potassium channels begin to close. This occurs around -80 mV and makes up the beginning of hyperpolarization.
3 thoughts on “Repolarization”