Threshold potential is the minimum potential difference that must be reached in order to fire an action potential. For most neurons in humans, this lies at -55 mV, so a signal to a resting cell must raise the membrane potential from -70 mV. The signal will have to overcome an even greater potential difference to reach threshold if the cell is hyperpolarized. Changes in potential that don’t reach -55 mV cause no change in the cell. Changes that exceed -55 mV do not differ in effect from those that just reach -55 mV since firing an action potential is an all-or-nothing event.
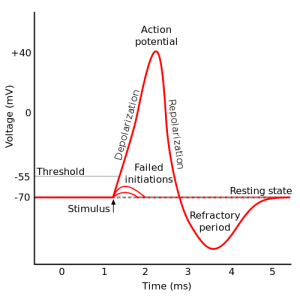
(“Action potential”)
4 thoughts on “Threshold Potential”