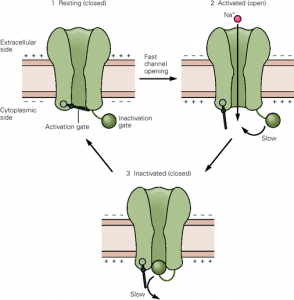
Voltage-gated sodium channels are a type of voltage-gated ion channel. These sodium channels in the axon of a neuron remain closed until the membrane potential rises to -55 mV. Following reaching threshold potential, the sodium channel opens and allows sodium ions to enter the cell. The sodium channel closes again when the region depolarizes to about +30 mV. The sodium channels become inactivated during repolarization. This means that no stimulus may reopen the channels. Sodium channels may be reopened during the relative refractory period, but this requires a greater-than-normal stimulus.
(“Voltage-gated sodium channel”)
4 thoughts on “Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels”