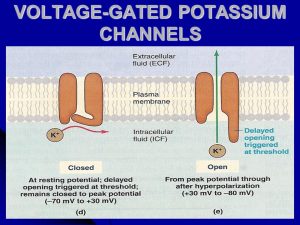
Voltage-gated potassium channels are a type of voltage-gated ion channel. These potassium channels line the axon of a neuron. They open when the membrane potential in the surrounding environment reaches about +30 mV. Potassium ions will flow out of the cell through the newly opened channels. This causes repolarization. Despite resting potential lying at -70 mV, the potassium channels will shut closer to -80 mV. This causes hyperpolarization.
(“Voltage-gated potassium channel”, 2016)
2 thoughts on “Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels”